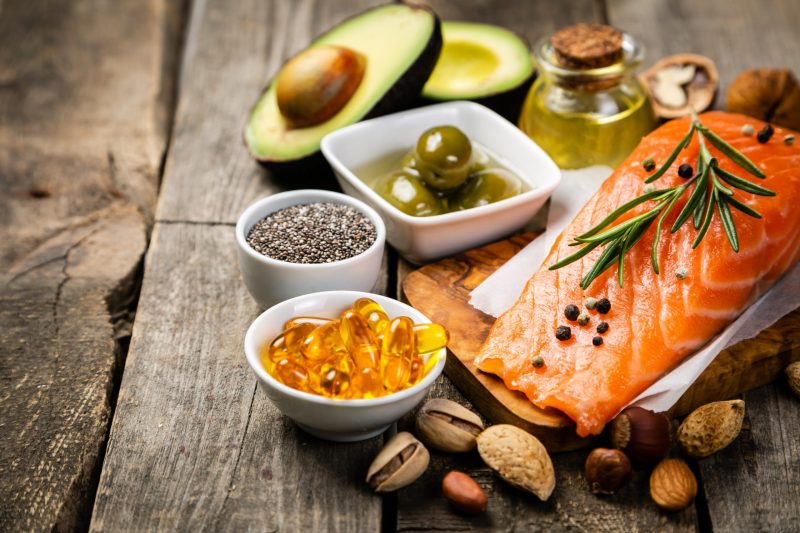
It’s not hyperbole. In many foods you eat, there are fats that heal, and there are fats that kill. Some dietary fats promote systemic inflammation, artery plaques, and disease. Some dietary fats fight inflammation, fight oxidative stress, and promote health in your brain, eyes, heart, and throughout your body.
As you look down a grocery store aisle, or even in your own pantry, can you distinguish the fats that kill vs. fats that heal? Do you know which foods are loaded with them? Do you know easy steps to avoid the killers and nourish your body with the healers?
If you don’t know yet, you certainly will by the end of this article. Take a look, and choose fats that heal while avoiding the ones that kill.
Fats that Kill
Let’s get the bad news out of the way first.
Fats that kill are everywhere in the modern diet. They promote inflammation, high amounts of dangerous oxidized cholesterol in your arteries, and modern health conditions. They also have another thing in common. The primary offenders are found in processed foods and fast foods.
Which fats kill?
Transfats
You may think you have a good handle on transfats. Thankfully, this is becoming more and more true. During the last decade, many Americans have become more aware of transfats, or partially-hydrogenated fats, and have begun weeding them out of their diets. Here’s what you need to know about deadly transfats.
- Transfats are produced when food chemists take a fat that is naturally liquid at room temperature, and add hydrogens to make it solid at room temperature. You can think of oil becoming margarine or Crisco. Beyond the obvious sources, through, these shelf-stable man made fats can be found in many processed foods. Look for “partially hydrogenated” or “hydrogenated” fats on your ingredient lists.
- Transfats can be listed as zero grams on a nutrition label anytime it only contains 0.4 grams or less per serving. Unfortunately, transfats cause harm even in very small amounts. So, do not trust the nutrition label. Look at the ingredient list and weed out all sources of transfats.
- Transfats cause harm to the human body by promoting inflammation and becoming oxidized. Inflammation is at the root of many modern health conditions. Furthermore, when cholesterol is oxidized, it becomes “sticky,” and sticks to artery walls and other cholesterol units, forming plaques.
Soybean Oil
Technically, soybean oil could be categorized as a transfat since it’s often hydrogenated, or as a polyunsaturated fat (below), since it is polyunsaturated in its natural state. However, it deserves its own “Fats that Kill” entry because it is incredibly detrimental to health, and it is found virtually in every processed food. Why? It’s cheap.
The biggest issue with soybean oil is that it is a concentrated source of omega-6 fats. Omega-6s fats, while necessarily in small amounts, become dangerous as our diets are loaded with them compared to omega-3 fats. These 2 types of fats are antagonists. The more omega-6 fats, the more problems. Soybean oil and concentrated omega-6 fats affect:
- Metabolic Health. Lab studies show that soybean oil is one of the most detrimental foods to metabolic health (1).
- Cardiovascular Health: Soybean oil has been shown to cause harmful abnormalities to cholesterol and triglycerides (2).
- Overall health and inflammation: Many studies have concluded that concentrated sources of omega-6 fats increase inflammation in the body (3).
Polyunsaturated Fats in Fried Foods
Polyunsaturated fats are vegetable oils that become easily oxidized in the arteries (again, these form plaques). They become especially dangerous when they are first used at very high heats when deep frying. Almost all deep-fried fast foods, chips, and fried snack foods are loaded with these harmful fats.
What’s more, they are also concentrated sources of omega-6 fats and contribute to the same problems listed above for soybean oil. Here is a list of polyunsaturated vegetable fats you should avoid and the amount of omega-6 fats in each of them per 1 tablespoon (in grams). For reference, a good goal for omega-6 fats in oils is no more than 2 grams, used sparingly.
- Safflower oil (10.1 gm Omega-6 per 1 tablespoon oil)
- Grapeseed oil (9.5)
- Vegetable Oil (7.9)
- Wheat Germ Oil (7.5)
- Corn Oil (7.3)
- Walnut Oil (7.3)
- Cottonseed Oil (7.0)
- Soybean (7.0)
- Sunflower Oil (5.4)
- Canola Oil (3.0)
Fats that Heal
Now, for some good news. There are many fats that heal your body, fight inflammation, and support health from your brains to your eyes to your heart. Here are the fats that heal:
Omega-3 Fats
Omega-3 fats come primarily from seafoods (specifically krill, fatty fish, seaweed, etc.) and to a lesser extent, vegetarian sources such as hemp seeds, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and more.
These incredibly healthful fats are a potent source of healing in the body. First, they tip the balance in favor of omega-3 fats versus omega-6 fats, which fights inflammation. They encourage great eye health and heart health. They also specifically support brain health. Omega-3s encourage:
- Cognitive Function: Researchers have found improved outcomes in at least one aspect of cognitive function studied (working memory, executive function, verbal memory, short-term memory, perceptual speed, etc.) when omega-3s are added to the diet. They concluded that omega-3 supplementation might have a positive effect on cognitive function and could be used as a preventive or therapeutic tool for cognitive decline in aged or older adults (4).
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Protection: TBI increases the levels of brain cell death and damage. A recent animal study found that omega-3 supplementation before traumatic damage offered neuroprotection (5). Additionally, it’s been established that dietary supplementation of omega-3s can reduce the oxidative stress and inflammation developed in the brain due after TBI by improving the survival of brain cells (6).
- Reductions in Cognitive Decline: Another recent study found that omega-3s may improve the immune factors that are important to brain function in those with cognitive decline (7). A study from 2017 found that omega-3 supplementation increased the unfolded protein response and improved amyloid-β phagocytosis by macrophages of patients with mild cognitive impairment (8). Lastly, another 2015 study found that omega-3 supplementation reduced brain inflammation in those with mild cognitive impairment (9).
Omega-9 Fats
There are 2 great oil options for omega-9 fats in your diet rather than omega-6 fats. Olive oil and avocado oil.
Olive oil can be used as a dressing/sauce over vegetables and other foods, as well as cooking at low and medium temperatures (it cannot be used to deep fry as it will reach its smoke point). Why use olive oil? It contains:
- Antioxidants Galore: Olive oil contains vitamin E, vitamin K, and hydroxytyrosol (HT). Hydroxytyrosol is a nutrient with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (10).
- Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Bacterial Compounds: Chronic inflammation is at the root of many modern chronic diseases, including cancer, heart disease, metabolic syndrome, Type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, arthritis, obesity and more. Olive oil contains an antioxidant called oleocanthal, which is strongly anti-inflammatory. In fact, it works similarly to anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen (11).
- Heart Protection: To support heart health, olive oil reduces inflammation and cholesterol oxidation in artery walls (12). It can also lower blood pressure and reduce the need for hypertension medications by up to 48% (13). What’s more, studies have found that those who consume olive oil have a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who don’t (14).
- Anti-Aging Nutrients: The most prominent fat in olive oil, oleic acid, is strongly anti-aging. What’s more, vitamin E, olive oil’s polyphenols, and vitamin K all support youthful cells, strong bones, improved gene expression and more (15).
- Brain Health Compounds: Olive oil may help remove Alzheimer-associated plaques from the brain, beta-amyloid plaques (16). In addition, studies have found that olive oil may improve cognition (17).
When you need an oil for higher temperature cooking, or for baking, use Avocado Oil.
Small Amounts of Medium Chain Triglycerides
Medium chain triglycerides (MCTs) are special fats, found in foods like coconut oil, that are medium in length, easy to digest, and offer benefits to the brain and body. What’s more, MCTs support ketone production and energy for those in the Keto Zone. The 2 main fatty acids in MCT oil and MCT oil powder are C8 and C10. These are readily converted to ketones and produce many beneficial health effects.
MCT Oil has been studied at length. Studies show it supports:
- Heart Health. The amazing MCTs in MCT Oil Powder have been shown to improve cholesterol profiles by decreasing LDL cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol (18).
- Reduced Inflammation. After a diet with MCTs, researchers have found significantly reduced C-Reactive protein, a marker for inflammation (19).
- Brain Health. Ketones produced from MCTs can reduce brain degradation from aging and improve brain function (20).
- Weight Loss. Consumption of MCTs has been correlated with reduced weight, body fat, and BMI in studies. What’s more, you won’t go hungry since they also increase satiety (21, 22).
- Blood Sugar Balance. MCTs can improve blood sugars and decrease insulin output, thereby improving health and fat breakdown (23).
- Healthy Digestion. Amazingly, MCTs can fight unhealthy yeasts while supporting an increase in healthy bacteria and absorption in the digestive tract (24).
- Energy and Athletic Performance. MCTs increase the energy output of the mitochondria in the cells in your body, significantly improving overall energy (25, 26).
Simple Ways to Choose Fats that Heal
It’s important to first recognize which are fats that heal and fats that kill. Then, take simple steps to improve your diet.
- Avoid processed foods at much as possible. Make as much of your food as you can at home. This is simple and important, but not easy. We all have busy schedules and homemade foods take time. But, you will know what ingredients go into your foods, and you can easily avoid the harmful ones.
- When you do buy commercial foods and condiments, look at every ingredient. Be on the lookout especially for soybean oil, any hydrogenated oils, and the concentrated omega-6 oils listed below.
- Avoid fast food, especially deep fried items, like the plague. Ask what oils are used in restaurants. Avoid foods that are fried or made with soybean oil specifically.
- When cooking, be careful what oils and fats you use. Use olive oil and avocado oil. Avoid the oils listed on the high omega-6 list.
- When taking omega-3 supplements (such as Krill oil), avoid supplements that are omega-3/omega-6 complexes. These complexes were first designed to deliver a healthy omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, but did not consider that most modern diets are already overloaded with omega-6 fat! There’s no need to add more omega-6s!
Listen to Dr. Colbert
Want to hear more? Of course you do! Check out our recent podcast on good fats and bad fats to hear insight from Dr. Colbert!
Bottom Line
Now you know: there are fats that heal and fats that kill. Use our guide and simple steps to consume fats that heal each day. Avoid the ones that are detrimental to your health. Take time to listen to Dr. Colbert speak on this subject. You can make a big difference with these small steps!