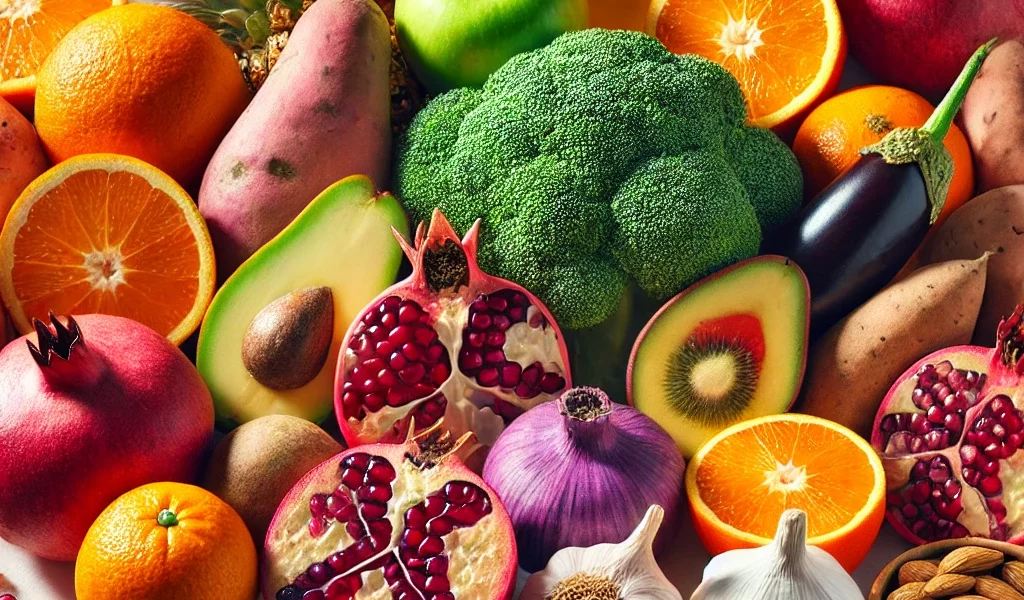
When it comes to enhancing immune function naturally, the role of diet cannot be overstated. A balanced diet rich in immune-boosting foods is fundamental to maintaining a robust and resilient immune system. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your daily meals, you can provide your body with the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants it needs to ward off illnesses and infections. Let’s delve deeper into how different foods contribute to immune health and why they should be a staple in your diet.
While Vitamin C often gets the spotlight for its role in immune support, there is a vast array of other foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that provide significant immune-boosting benefits. To maintain a strong immune system, it’s crucial to incorporate a variety of these nutrient-rich foods into your daily diet. Let’s explore some of these powerful foods and understand how their unique components contribute to enhancing immune function.
Pomegranate: A Powerful Antioxidant Source
Pomegranates are a rich source of antioxidants, particularly polyphenols like punicalagins and anthocyanins. These compounds have been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects. Antioxidants help protect the body from oxidative stress, which can damage cells and weaken the immune system.
Research indicates that pomegranate extract can enhance the immune system by increasing the activity of natural killer (NK) cells, which play a crucial role in the body’s defense against infections and cancerous cells nally, pomegranates are known to promote gut health, which is closely linked to immune function, by fostering a healthy gut microbiome.
Apples: Rich in Quercetin
Apples are a great source of quercetin, a flavonoid with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin has been studied for its ability to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, which can help protect the body from various infections and diseases.
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that quercetin supplementation enhanced immune response in participants and reduced the incidence of respiratory infections . Incorpples into your diet can provide a natural source of quercetin, supporting overall immune health and helping the body to fight off pathogens more effectively.
Sweet Potatoes: High in Vitamin A
Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, which the body converts into Vitamin A. This essential vitamin is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, the body’s first line of defense against pathogens. Vitamin A also plays a role in the development and regulation of the immune system, particularly in maintaining the function of T-cells, which are critical for immune response.
Studies have shown that a diet high in Vitamin A can enhance the body’s ability to fight off infections and reduce the severity of illnesses . Consuming foodst potatoes, carrots, and other beta-carotene-rich vegetables can provide your body with the necessary nutrients to maintain a robust immune system.
Garlic: Nature’s Antibiotic
Garlic has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties, particularly its ability to boost the immune system. Garlic contains allicin, a sulfur-containing compound known for its antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties. Allicin has been shown to enhance the immune response by stimulating the activity of various types of immune cells, including macrophages and natural killer cells.
A study published in Advances in Therapy found that participants who took a garlic supplement experienced fewer colds and recovered faster compared to those who took a placebo . Including garlic in yourther raw or cooked, can provide these powerful immune-enhancing benefits.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Full of Immune-Enhancing Compounds
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and Brussels sprouts are not only rich in vitamins and minerals but also contain unique compounds such as sulforaphane. Sulforaphane has been shown to activate antioxidant pathways and enhance the immune system’s ability to fight off toxins and pathogens.
A study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry highlighted sulforaphane’s ability to boost the immune system’s response to bacterial infections by activating immune cells . Consuming a variety of cruciferoues provides a range of nutrients that support overall immune health and protect against disease.
Nuts and Seeds: Packed with Immune-Supportive Nutrients
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, sunflower seeds, and flaxseeds, are rich in essential nutrients, including Vitamin E, zinc, and healthy fats. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cell membranes from oxidative damage, while zinc is vital for immune cell development and function.
Research has shown that Vitamin E can enhance immune function, particularly in older adults, by boosting the activity of T-cells . Incorporating a handful of nuts and seeds daily diet can provide these critical nutrients, supporting both innate and adaptive immunity.
Fermented Foods: Probiotics for Immune Health
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are rich in probiotics—live beneficial bacteria that support gut health. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a well-functioning immune system, as it helps prevent harmful pathogens from colonizing the gut and entering the bloodstream.
Research has demonstrated that regular consumption of probiotic-rich foods can enhance the immune system’s response to infections and improve overall digestive health . Including these foods in your diet can promote a ba environment, supporting immune function and protecting against illness.
2. Take Immune-Supporting Supplements
Certain supplements can help strengthen your immune system by providing nutrients that may be lacking in your diet. Some of the most effective immune-boosting supplements include:
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is crucial for immune function, and deficiency is linked to increased susceptibfility to infection. Studies suggest that Vitamin D supplementation can enhance the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages—white blood cells that are critical parts of immune defense .
- Zinc: Zinc is another vital nutrient for immune health, playing a key role in the development and function of immune cells. A meta-analysis found that zinc supplementation reduces the incidence of infections, particularly in the elderly and children .
3. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and immune function. Water helps carry oxygen to your body cells, which results in properly functioning systems. It also aids in the removal of toxins from the body, which can help prevent infections. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and more if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
4. Prioritize Sleep
Quality sleep is one of the most effective natural ways to boost your immune system. During sleep, the body releases cytokines, a type of protein that targets infection and inflammation, effectively creating an immune response. Lack of sleep can decrease the production of these protective cytokines, weakening the immune response.
Research shows that individuals who do not get adequate sleep are more likely to get sick after being exposed to a virus, such as the common cold virus . For optimal immune function, aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night.
5. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity is not only great for overall health but also boosts the immune system. Regular moderate exercise can help reduce inflammation and promote the healthy turnover of immune cells.
A study published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology found that regular moderate exercise can reduce the risk of illness by enhancing immune function. Exercise helps flush bacteria out of the lungs and airways, reduce stress hormones, and increase circulation of white blood cells .
6. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can negatively impact immune function, making you more susceptible to infections. Stress induces the production of cortisol, which can suppress the immune system’s effectiveness. Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help maintain a strong immune system.
Studies have shown that people who meditate regularly have higher levels of antibodies and a stronger immune response . Incorporating stress-reducing practices into your daily routine can greatly support your overall immune health.
7. Maintain a Healthy Gut
A large part of the immune system is located in the gut, where beneficial bacteria play a key role in defending against pathogens. Consuming probiotics and prebiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn supports immune function.
- Probiotics, such as those found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods, help populate the gut with beneficial bacteria.
- Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, feed these beneficial bacteria, promoting a balanced gut environment.
A healthy gut can prevent harmful pathogens from entering the bloodstream, thus enhancing overall immune function. Research has shown that probiotics can help reduce the duration of respiratory infections and support the immune system’s response to illness .
By incorporating these seven natural strategies into your daily routine, you can effectively enhance your immune function and support overall health. Remember, a healthy immune system is your best defense against illness. Whether it’s through diet, supplements, or lifestyle changes, taking proactive steps to boost your immunity will help you live your best, healthiest life.
References:
- Hemilä, H. (2017). Vitamin C and Infections. Nutrients, 9(4), 339.
- Aranow, C. (2011). Vitamin D and the Immune System. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 59(6), 881-886.
- Prasad, A. S. (2008). Zinc in Human Health: Effect of Zinc on Immune Cells. Molecular Medicine, 14(5-6), 353-357.
- Cohen, S., Doyle, W. J., Alper, C. M., Janicki-Deverts, D., & Turner, R. B. (2009). Sleep Habits and Susceptibility to the Common Cold. Archives of Internal Medicine, 169(1), 62-67.
- Nieman, D. C., & Wentz, L. M. (2019). The Compelling Link Between Physical Activity and the Body’s Defense System. Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 2299.
- Black, D. S., & Slavich, G. M. (2016). Mindfulness Meditation and the Immune System: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1373(1), 13-24.
- Hao, Q., Dong, B. R., & Wu, T. (2015). Probiotics for Preventing Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2).